THE MOST EXPERIENCED IN THE SPRINGFIELD AREA
WHAT IS RADON?
What you should know
Radon is a naturally occurring gas that comes from the decay of uranium in the soil and can have a big impact on indoor air quality and your health. You can't see or smell it, and radon can build up inside homes, buildings and schools to dangerous levels. Exposure to high levels of radon can cause lung cancer. Learn about radon, how it affects lung health and what you can do about it.
Radon is the second leading cause of lung cancer in the United States, responsible for thousands of deaths each year. Exposure to radon causes no immediate symptoms, but the long-term threat of lung cancer is significant to everyone. People who have never smoked make up approximately 2,900 of the estimated 21,000 radon-related lung cancer deaths each year.
The health hazard comes from radioactive particles released when radon decays. These particles can be inhaled into the lung and bombard your cells with dangerous, cancer-causing radiation. Smoking and radon exposure can separately increase the risk of lung cancer. But if you smoke, know that exposure to both greatly enhances the risk of lung cancer.
There is no debate about radon being a lung carcinogen in humans. All major national and international organizations that have examined the health risks of radon agree that it is a lung carcinogen. The scientific community continues to conduct research to refine our understanding of the precise number of deaths attributable to radon. The National Academy of Sciences has estimated that radon causes about 15,000 to 22,000 lung cancer deaths annually. Major scientific organizations continue to believe that approximately 12% of lung cancers annually in the United States are attributable to radon.
Now, my job is not to convince you of the damaging effects of radon, I'll let the scientists work on that....
My goal is to provide fast, accurate, dependable results to my client who wants to know what their property or potential property's radon levels are.
Radon testing devices are placed in accordance with IEMA's measurement protocol and exposed to the indoor air for a minimum of 48 hours. These devices are then picked up and the data is entered into a computer program that interprets this data and converts it into picocuries, the unit of measure when measuring radon levels in a home.
If the property test results come back at 4.0 pCi/L or higher, it is recommended that a mitigation system be installed to reduce the radon levels down to an acceptable level.
(In Illinois its 3.9pCi/L or lower, in extreme cases mitigation is only required to get it as low as reasonably possible.)
Once a system is installed, it is recommended to test again to ensure the system is effective in reducing the radon levels.
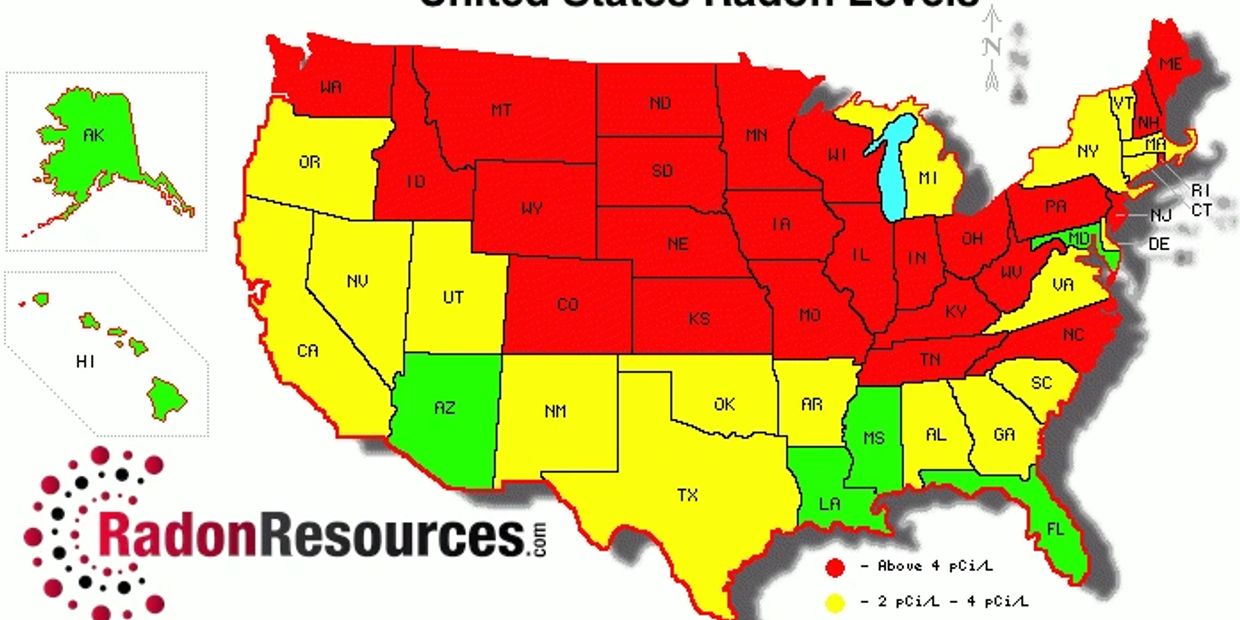
YOU HAVE RADON IN YOUR HOUSE RIGHT NOW....
Everybody in central Illinois is exposed to radon gas in their houses. Regardless of the type of house, new or old, basement, slab or crawl, mitigation or not.
The question is, at what level?
ACTS & LAWS IN ILLINOIS
ILLINOIS RADON AWARENESS ACT
The Illinois Radon Awareness Act, which took effect January 1, 2008, requires sellers of a home to provide anyone buying their home, condominium or other residential property in Illinois with information about indoor radon exposure and the fact that radon is the leading cause of lung cancer in non-smokers and the second leading cause of lung cancer overall. The new law doesn’t require that homes be tested for radon prior to the sale or that radon remediation work be conducted if test results show high levels of radon. However, under the new law, if a radon test has been conducted on the home those results must be provided to the buyer.
The Illinois Emergency Management Agency (IEMA) strongly recommends ALL homebuyers have an indoor radon test performed prior to purchase or taking occupancy, and mitigation if elevated levels are found.
The buyer, seller and realtor must all sign a disclosure agreement stating that all parties understand the dangers of radon and their obligations under Illinois law.
LAW REQUIRES RADON TESTING IN DAY CARE CENTERS
Parents of children in day care will be better informed about levels of radon in their child’s facility under a new law that took effect Jan. 1, 2013. Licensed day care centers and day care homes are now required to test for the radioactive gas, and beginning Jan. 1, 2014, day care centers will need to show proof the facility has been tested for radon within the last three years as part of the initial application or license renewal process.
ILLINOIS LAW TO PROTECT RENTERS
A new law that went into effect on Jan. 1, 2012, will help people who rent apartments, condominiums or houses access information about radon levels in their homes. The Illinois Emergency Management Agency’s (IEMA) radon program is offering guidance to help renters better understand radon hazards and their rights under this new law.
Public Act 97-0021, which was approved by the Illinois General Assembly this spring and signed by Gov. Quinn on June 28, 2011, requires owners of rental units to inform renters in writing before a lease is signed if the rental space has been tested for radon and that a radon hazard may exist. If the rental unit hasn’t been tested, a renter can conduct a do-it-yourself radon test or ask the owner to test by hiring a licensed radon contractor. If a renter conducts a radon test in the rental unit and results show high radon levels, the renter should inform the building owner in writing.
IEMA recommends that all rental units below the third floor be tested for radon.
